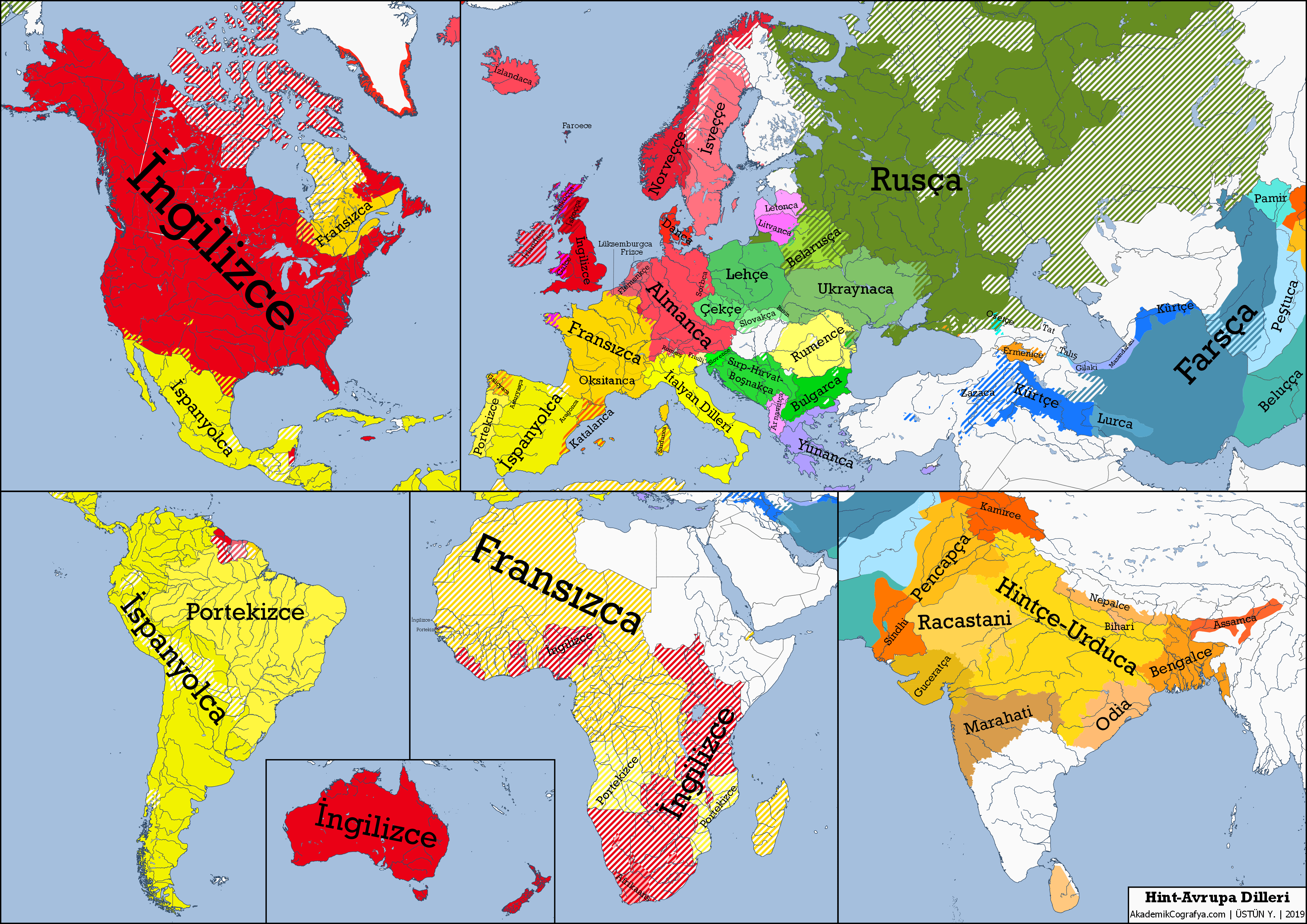
The Indo-European languages form a remarkable family of over 400 languages spoken by more than 40 percent of the world’s population today. Recent studies have traced their origins back approximately 6,500 years to the people of the Caucasus Lower Volga region in present-day Russia, revealing intricate connections to the iconic Yamnaya culture. These breakthroughs in understanding the origins of Indo-European languages were fueled by genetic studies that illuminate the language dispersal history and migrations of ancient peoples. Research indicates that these early speakers mixed with various groups, contributing significantly to the linguistic tapestry we see today. As scholars piece together the ancestry of these languages, they unveil the rich cultural traditions that accompanied the spread of this linguistic legacy across vast territories.
The linguistic family that encompasses the roots of many modern tongues is known as the Indo-European languages, which have distinct connections to ancient peoples and cultures. Complex studies have revealed that speakers of these languages originated in a region that now encompasses parts of Russia, particularly through the fascinating lens of genetic analysis. By exploring the influences of the Yamnaya civilization and the enigmatic Caucasus Lower Volga groups, researchers are unraveling the intricate history of language dispersal across Europe and Asia. These efforts strive not only to understand the languages themselves but also the cultural exchanges that have shaped human communication over millennia. As this research progresses, it sheds light on the profound links between language, identity, and migration.
Origins of Indo-European Languages
The origins of Indo-European languages trace back to the Caucasus region approximately 6,500 years ago, where a group known as the Caucasus Lower Volga people identified as the speakers of this ancient tongue. This significant finding has captivated scholars and linguists seeking to understand the dispersal of language across continents. The research indicates that these language pioneers were not only located in present-day Russia but also mingled with neighboring populations, contributing to the rich tapestry of linguistic evolution that characterizes many modern languages today.
By examining archaeological findings alongside sophisticated genetic studies, researchers have pieced together a comprehensive narrative regarding the birth and spread of the Indo-European language family. The Yamnaya culture, recognized as a pivotal force in this linguistic development, showcases how dynamic cultural exchanges and migrations can shape language history. As the Yamnaya people ventured out of their homeland into vast territories, they took their language and traditions with them, paving the way for the Indo-European languages that we know today.
Yamnaya Culture and Its Impact on Language
The Yamnaya culture emerged as a key player in the dissemination of proto-Indo-European languages, characterized by their nomadic pastoralist lifestyles and innovative agricultural practices. Renowned for their distinctive burial mounds, or kurgans, the Yamnaya left behind an enduring archaeological legacy that speaks to their complexity as a society. Their ability to herd animals effectively and utilize ox-drawn wagons was unprecedented, granting them enhanced mobility that enabled extensive migrations. This movement across the Eurasian steppes significantly influenced the spread of their languages throughout Europe and Asia.
In addition to their role in language dispersal, the Yamnaya people are believed to have played a crucial part in the genetic landscape of modern Europeans. By intermingling with local populations, they altered the genetic makeup of the areas they settled, leaving a lasting impact that resonates in contemporary genetic studies. The interactions between the Yamnaya and the diverse groups they encountered were not merely about language but encompassed a rich exchange of cultural practices, customs, and technologies that shaped civilizations for millennia.
The Genetic Study of Indo-European Speakers
Recent genetic studies have provided critical insights into the ancestry of Indo-European speakers, revealing complex patterns of migration and mixing. By analyzing ancient DNA from various archaeological sites, researchers have mapped the genetic contributions of different populations, offering a clearer understanding of the interconnections among ancient cultures. The evidence aligns well with the hypothesis suggesting that the Yamnaya were instrumental in the spread of Indo-European languages, prompting a reevaluation of long-held beliefs about language origins.
This groundbreaking work is characterized by its comprehensive approach to understanding the links between genetics and language. As researchers continue to uncover and analyze ancient remains, the intricate relationships among populations become apparent, showcasing a network of interactions that shaped linguistic patterns across regions. The incorporation of genetic data into the study of language allows for a multidisciplinary perspective that enhances our grasp of how language evolved amidst shifting demographic landscapes.
Cognitive and Cultural Implications of Language Dispersal
The dispersal of Indo-European languages not only signifies a linguistic journey but also reflects deeper cognitive and cultural transformations in human societies. Languages carry with them intricate ways of thinking and understanding the world, and their diffusion into new territories often leads to the redefinition of cultural identities. The process of language adoption and adaptation can foster innovation and the sharing of ideas, contributing to advancements in areas such as governance, technology, and social structures.
Culturally, the spread of language invariably leads to the creation of new social narratives and mythologies, influencing art, religion, and daily practices within communities. As populations adopted these languages, they simultaneously embraced a broader cultural exchange, resulting in a rich tapestry of traditions that enriched the human experience. The Indo-European language family thus offers a compelling framework for exploring how language serves as a vehicle for cultural integration and transformation.
The Role of Archaeology in Understanding Language History
Archaeology plays a pivotal role in uncovering the histories and narratives associated with languages, particularly the Indo-European family. By excavating sites related to the Yamnaya culture and their descendants, researchers gather invaluable artifacts, burial practices, and settlement patterns that elucidate how ancient peoples lived and communicated. These archaeological insights provide a backdrop for understanding the contexts in which languages were spoken and the social dynamics at play.
Moreover, the artifacts discovered at these sites often include items of daily use, religious significance, and cultural value, which further illustrate how language and culture intermingle. The findings from kurgans and other burial sites are particularly potent, offering a glimpse into the beliefs and customs of the Yamnaya people. As archaeology continues to evolve with technological advancements, it promises to unravel even more about the interplay between human societies and their languages, thereby enriching our understanding of the past.
Tracing Linguistic Evolution through Comparative Studies
Comparative studies have historically been vital in tracing the evolution of languages, especially in the context of the Indo-European family. By examining similarities and differences across related languages, scholars can infer historical connections and reconstruct aspects of the proto-Indo-European tongue. This method not only reveals the linguistic features that have persisted through centuries but also highlights the changes that languages have undergone due to geographical and cultural influences.
The comparative approach empowers researchers to establish timelines for language divergence and convergence, illustrating how languages evolve in response to social and environmental changes. As languages spread and intersect through migration, factors such as trade, conquest, and intermarriage lead to linguistic borrowing and innovation, contributing to the rich diversity of languages we see today. Understanding the mechanisms of this evolution offers profound insights into the human story and the adaptability of languages in shaping human experience.
The Importance of Interdisciplinary Collaboration
The study of language origins and dispersal is inherently interdisciplinary, requiring collaboration among linguists, archaeologists, geneticists, and anthropologists. This convergence of expertise fosters a holistic perspective on the cultural and biological factors influencing language development. As researchers from various fields come together, they can better address the complexities of language history and the myriad influences that have shaped it across generations.
Collaborative efforts yield novel methodologies that integrate linguistic analysis with genetic data and archaeological findings, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of ancient populations. By sharing insights and methodologies, scholars can refine their hypotheses, test new frameworks, and ultimately derive conclusions that reflect the multifaceted nature of human communication. This collective approach is essential as it allows for the unraveling of intricate narratives surrounding the origins of languages and the cultural legacies they carry.
The Future of Research on Indo-European Languages
As research on Indo-European languages continues to advance, emerging technologies and methodologies stand to revolutionize our understanding of linguistic history. The integration of genetic sequencing with linguistic research offers unparalleled opportunities to trace the movements and interactions of ancient societies. With each new discovery, researchers can deepen their insights into how languages have spread and evolved over time, and the anthropological implications of these changes.
Moreover, modern technologies, including machine learning and data analysis, are becoming increasingly important in the study of language and genetics. These tools can aid in creating predictive models and simulations to explore potential language scenarios, thereby enhancing our predictive capabilities about language evolution. The future of this research promises to uncover even more about the dynamic and intricate histories of human language, significantly enriching our understanding of human civilization.
Challenges and Controversies in Language Research
Despite promising advancements in the study of Indo-European languages, researchers face numerous challenges and controversies that can complicate their work. Disagreements often arise regarding the methodologies employed to trace linguistic lineages—some scholars advocate for a more traditional linguistic approach, while others emphasize the importance of integrating genetic information. Navigating these differing perspectives requires a keen understanding of both linguistic nuance and genetic complexity.
Additionally, geopolitical factors can hinder collaboration and data sharing among researchers from different countries. The ongoing conflict in regions like Ukraine has disrupted scholarly communication, making it difficult to conduct joint studies and share vital research findings. Overcoming these obstacles will be essential for advancing our knowledge of language origins and fostering a more inclusive narrative that embraces the contributions of diverse populations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the origins of Indo-European languages and how are they connected to the Yamnaya culture?
The origins of Indo-European languages have been traced back to the Caucasus Lower Volga region, where the Yamnaya culture flourished approximately 6,500 years ago. This culture is believed to be a primary source of the Proto-Indo-European language, from which over 400 modern languages descend. Researchers utilized genetic studies to trace these language roots and confirmed that the Yamnaya people mixed with other groups in the region, aiding the spread of these languages across Europe and beyond.
How did genetic studies contribute to understanding the dispersal history of Indo-European languages?
Genetic studies have proven vital in understanding the dispersal history of Indo-European languages by identifying the Caucasus Lower Volga people as the early speakers of ancestral tongue. Landmark research revealed their genetic lineage and how it spread from their homeland in present-day Russia to regions across Europe, confirming hypotheses about language diffusion patterns alongside migration and cultural exchange.
Who were the Caucasus Lower Volga people and what role did they play in the development of Indo-European languages?
The Caucasus Lower Volga people were an ancient population that lived around 6,500 years ago in what is now Russia. They are recognized as the originators of the Indo-European languages due to their significant role in the early formation and dissemination of a proto-Indo-European language, which later evolved into many contemporary languages spoken today. Their interactions and genetic mixing with other nearby populations facilitated the growth and spread of this language family.
What is the significance of the Yamnaya culture in relation to Indo-European languages?
The Yamnaya culture holds immense significance as it is considered a primary contributor to the spread of Indo-European languages. Characterized by their nomadic pastoral lifestyle, the Yamnaya people are credited with technological advancements such as horse-riding and wagon use, which enabled their migration and cultural exchange abilities. This culture’s impact on language dispersal has been substantiated by genetic studies connecting Yamnaya ancestry to various Indo-European languages across Europe and Asia.
How did archaeological findings support theories about the spread of Indo-European languages?
Archaeological findings, such as burial sites and artifacts from the Yamnaya culture, have supported theories about the spread of Indo-European languages by providing context to the lifestyle and migration patterns of these ancient peoples. The discovery of kurgans, or burial mounds, across different regions has helped researchers trace the movement of the Yamnaya and their language, showing a direct link between cultural practices and language dispersal.
What are the challenges researchers face when studying the origins of Indo-European languages?
Researchers studying the origins of Indo-European languages face challenges such as geopolitical tensions, particularly in regions like the Caucasus and Ukraine, which can complicate collaborative efforts. Additionally, the complexity of linguistic evolution, genetic mixing between populations, and the interpretation of archaeological evidence creates a multifaceted puzzle that requires multidisciplinary approaches and careful analysis to decipher.
How do modern studies of genetics inform our understanding of ancient Indo-European languages?
Modern genetic studies have profoundly informed our understanding of ancient Indo-European languages by providing insights into the ancestry and migration patterns of populations such as the Yamnaya. By analyzing ancient DNA samples, researchers can trace genetic markers that correspond to linguistic trends, demonstrating how genetics and language evolved together through interactions and movements of diverse groups across Europe and into Asia.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Research identifies the Caucasus Lower Volga people as the originators of the Indo-European languages, which are spoken by over 40% of the global population. |
| DNA evidence places these ancestral speakers in present-day Russia around 6,500 years ago, during the Eneolithic period. |
| The Yamnaya people, previously thought to be the sole originators, were involved in the dissemination of proto-Indo-European languages. |
| The research provides genetic links to Anatolian languages, suggesting a complex ancestry involving mixing populations. |
| A separation in findings was noted due to the Russia-Ukraine war, leading to collaborative work impeded by ongoing conflict. |
| Burial traditions observed in kurgans connect the cultural practices of the Yamnaya and their Caucasian ancestors. |
Summary
The new research sheds light on the origins of Indo-European languages, identifying the Caucasus Lower Volga people as crucial contributors to the linguistic family that encompasses over 400 languages. This revelation not only provides insights into ancient human migrations but also connects linguistic evolution with genetic ancestry, highlighting a rich tapestry of cultural exchange that shaped much of Eurasia. Understanding the history of Indo-European languages allows us to appreciate the complexities and interconnections of ancient civilizations.